🏭 Architecture
This chapter explains how the different parts of the Metajob headless architecture work together — from backend setup and plugins to UI themes and the frontend core. It covers the communication flow, configuration, and deployment strategies within the monorepo structure.
1.🔄 Overview of the Headless Architecture
Our architecture is designed around a modular, themeable, and scalable monorepo, combining the power of:
-
Strapi (as the headless CMS backend),
-
Next.js (as the frontend framework),
-
Reusable plugins ( metajob-backend),
-
Pluggable UI themes (metajob-theme), and
-
A shared configuration system (padma.settings.ts) that connects everything together.
🔧 Technologies Used
| Layer | Tech Stack |
|---|---|
| Backend | Strapi + Custom Plugin |
| Frontend | Next.js (App Router) |
| Config Layer | padma.settings.ts |
| Theme System | Custom Theme Packages |
| Monorepo | Managed with workspaces |
2.📦 Monorepo Project Structure
# Main Next.js frontend (App router)
├── packages/ # All UI themes (published as npm packages)
│ └── metajob-theme/
├── package.json # Workspace setup with theme dependency
├── padma.settings.ts # Configuration to inject UI theme
├── apps/
├── frontend/
│── backend/ # Strapi backend
│ └── plugins/
│ └── metajob-backend/ # Custom plugin (also published to npm)
│
- apps/backend/: Strapi-based backend with pluggable custom plugins.
### 3.🔌 **Plugin Integration: Backend Layer**
The first part of the system to run is the Strapi backend, which includes the metajob-backend plugin. This plugin handles custom content types, controllers, routes, and services necessary for the frontend to function correctly.
How it works:
- metajob-backend is loaded as a Strapi plugin.
- It exposes custom endpoints for jobs, companies, candidates etc.
- The plugin is designed to be published and reused across different projects.
<a
href="/products/metajobs/architecture-1.png"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
<Image
src="/products/metajobs/architecture-1.png"
alt="Hello"
width={900}
height={1500}
/>
</a>
A backend request flow diagram showing how metajob-backend integrates into
Strapi and how it exposes APIs
### 4. ⚙️ **Connecting Backend to Frontend**
Once the backend is running, the Next.js frontend (core) consumes its data via API calls.
- The core/ app fetches content from Strapi using the endpoints exposed by metajob-backend.
- All data is fetched either statically (via generateMetadata and getStaticProps) or dynamically based on routing.
- This ensures a fast, SEO-optimized frontend with dynamic content rendering.
<a
href="/products/metajobs/architecture-2.png"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
<Image
src="/products/metajobs/architecture-2.png"
alt="Hello"
width={900}
height={1500}
/>
</a>
Request-response cycle: Frontend → Strapi API → Response → Render
### 5. 🎨 **Theme System and UI Integration**
The UI is built in a themeable way, where multiple UI packages (themes) can be added and used dynamically.
- metajob-theme is the default UI theme, installed via package.json.
- The theme is passed into the frontend through padma.settings.ts.
- The frontend app uses the theme components for rendering layouts, detail pages, and shared UI.
Theme Swapping:
```ts
export const settings = {
activeTheme: "@jstemplate/metajob-theme", // Default active theme
};
export const themeResolver: Record<string, () => Promise<any>> = {
"@jstemplate/metajob-theme": () => import("@jstemplate/metajob-theme"),
};This architecture allows teams to:
-
Build and switch themes easily
-
Extend or override components per project
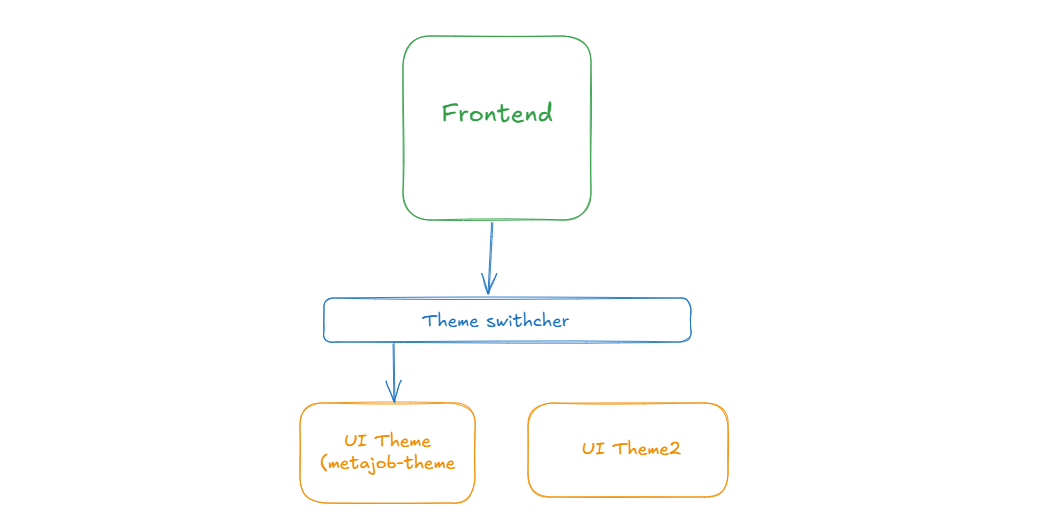
Injecting metajob-theme into core
6. 🔁 Data Flow: End-to-End Communication
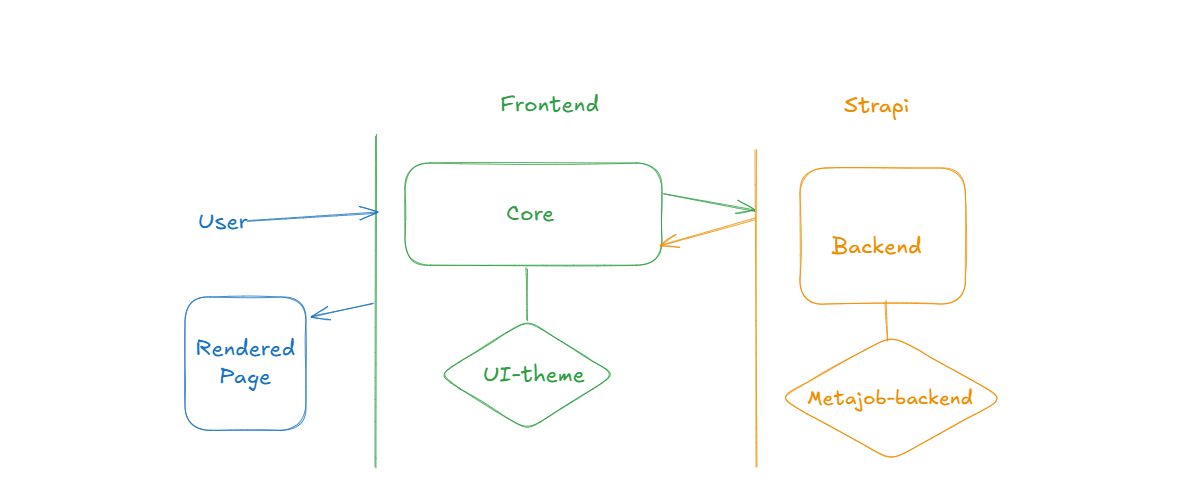
Here’s the complete data flow through the system:
-
Backend Initialization: Strapi loads with metajob-backend plugin.
-
API Exposure: The plugin provides endpoints for public/private data.
-
Frontend Boot: Next.js f app initializes.
-
Theme Injection: padma.settings.ts connects the UI theme.
-
Data Fetching: frontend app fetches from Strapi APIs using the plugin's endpoints.
-
Rendering: UI components render the fetched data using the active theme.
-
Error Handling: Implement error handling for API requests to ensure a smooth user experience.